Genetics
and the
Cavalier King Charles Spaniel
-
 Estimated
Breeding Values
Estimated
Breeding Values - Genetics of SM -- By Dr. Sarah Blott
- Research News
- Related Links
- Veterinary Resources
The cavalier King Charles spaniel (CKCS) breed is susceptible to numerous inherited disorders. Here is a list of the main hereditary disorders which either are unique to CKCSs or are more common in them than most other breeds (researcher veterinarians call these “pre-disposed to”):
Mitral valve disease (MVD)
Chiari-like malformation (CM)
Syringomyelia (SM)
Low blood platelets (idiopathic asymptomatic
thrombocytopenia)
Primary secretory otitis media (PSOM) – glue ear
Pneumocystis pneumonia
Episodic falling syndrome
Curly coat
syndrome
Dry eye syndrome
Fly catchers syndrome
Deafness –
progressive hereditary hearing loss
Cerebellar infarcts – strokes
Xanthinuria
Eosinophilic stomatitis
Masticatory muscle myositis
(MMM)
Obesity
Chronic pancreatitis
Exocrine pancreatic
insufficiency (EPI)
Brachycephalic airway obstruction syndrome (BAOS)
Intervertebral disk disease (IVDD)
Diabetes mellitus
Hip dysplasia
(HD)
Idiopathic epilepsy
Chronic kidney disesase
Muscular
dystrophy
Patellar luxation
Temporomandibular joint dysplasia
All of these are discussed in some depth, elsewhere on this website. Check the list in the left column to go to any one of the topics.
Estimated Breeding Values
- What are EBVs?
- The importance of using objective data
- Can a dog's EBV change?
- How are EBVs to be used?
- The advantages of using EBVs
What are EBVs?
An “estimated breeding value” (EBV) is a statistical numerical prediction of the relative genetic value of a particular dog (male or female) available for breeding. EBVs are used to rank breeding stock for selection, based upon the genetic risk of each dog with regard to one or more specified traits. An EBV therefore is a calculated estimate of heritability for each trait being considered, relative to the EBVs of other dogs in the breeding population. EBVs are limited to the genetic liabilities and do not include environmental conditions subsequent to birth.
EBVs for cavalier King Charles spaniels are intended to be each dog’s genetic risk of disease – initially syringomyelia and early-onset mitral valve disease – relative to the rest of the available breeding stock.
EBVs are calculated by compiling as much objective information about each dog as possible, including health test data, together with its pedigree information and physical characteristics. The sum of this data is called the dog’s “phenotype” – what can be observed and measured with respect to the disease(s). A dog’s phenotype will consist of both genetic and non-genetic components.
The importance of using objective data
To be useful to breeders, EBVs must be accurate and unbiased. This accuracy applies to both the particular dog being examined as well as the breeding population as a whole. For EBVs to be accurate, the calculators constantly need as much information, particularly health test data, on as many cavaliers as possible.
Can a dog’s EBV Change?
EBVs are based upon the data available for estimating them. As new information is collected, about the particular dog or its relatives, its EBV can be re-calculated to improve the accuracy of its estimate. Initially, an off-spring’s EBV is the sum of its sire’s and dam’s scores, divided by two. As more and more of the dog’s health test data and other information is acquired, the EBV will change.
How are EBVs to be used?
The EBV system is evolving and currently in its early stage,
and presently only among cavaliers in the United Kingdom.
 The
UK Kennel Club has introduced its EBV database program, called
Mate Select, which is designed to generate EBVs. Mate Select is intended to enable breeders to assess the impact that a proposed mating will have on
the genetic diversity of the offspring and maximize the chances of producing
healthy puppies while also having the optimum impact on the breed’s genetic
diversity. In the UK, once EBVs are assigned , breeders can compare the
EBVs of the breeding stock, to determine which cavaliers may be expected to best
meet the SM and MVD breeding protocols when bred.
The
UK Kennel Club has introduced its EBV database program, called
Mate Select, which is designed to generate EBVs. Mate Select is intended to enable breeders to assess the impact that a proposed mating will have on
the genetic diversity of the offspring and maximize the chances of producing
healthy puppies while also having the optimum impact on the breed’s genetic
diversity. In the UK, once EBVs are assigned , breeders can compare the
EBVs of the breeding stock, to determine which cavaliers may be expected to best
meet the SM and MVD breeding protocols when bred.
EBVs will be an important, objective (and hopefully unbiased) tool for breeders to use in the process of selecting breeding stock. Their aim is to improve the accuracy of breeding stock selection decisions, resulting in reducing the risk of genetic disease in each succeeding generation. Sarah C. Blott, a geneticist at the UK's Animal Health Trust, said: “Science will completely transform dog breeding in the future, allowing breeders to make choices about which dogs to mate based on scientific information that will be available from the Kennel Club.”
Of course, it will remain the decision of each breeder as to whether to use EBVs and Mate Select. Hopefully, more breeders will take advantage of this information than have been following the currently available breeding guidelines, such as the mitral valve disease breeding protocol and the syringomyelia breeding protocol, both of which have been largely ignored, at least in the United States.
The advantages of using EBVs
 Dr. Clare Rusbridge, UK veterinary neurologist has compared
the current SM breeding protocol to EBVs for
combating syringomyelia on
her blog in 2011:
Dr. Clare Rusbridge, UK veterinary neurologist has compared
the current SM breeding protocol to EBVs for
combating syringomyelia on
her blog in 2011:
"It has been five years since the introduction of the International Breeding guidelines for Syringomyelia in 2006. These provided an interim measure for breeders based on existing evidence with a common sense approach until there was better understanding for this complex condition. A Mate Select Scheme that generates estimated breeding values is considered superior. Some breeders consider themselves capable of making their own decisions based on their wealth of breeding experience and knowledge of their own dogs’ MRIs. However CMSM is a complex trait which means that knowing the health status of close relatives is unlikely to be sufficient for predicting the disease free status of the offspring. Information about generations of dogs needs to be taken into account."
In a 2010 article about evaluating hip scores of Labrador retrievers, the UK authors, Thomas W. Lewis, Sarah C. Blott, and John A. Woolliams, explained the advantages of using EBVs for selecting breeding stock:
"The presented results have demonstrated that the availability of EBV through routine evaluations of the hip score data would hasten progress in alleviating the problem of hip dysplasia via increases in selective accuracy compared to selection based on phenotype alone [for example, MRI scans or heart testing]. However the benefits of EBV extend beyond the simple comparisons of accuracy for a recently scored dog:
(i) the EBV for an individual, unlike its phenotypic score, will further increase in accuracy over time by utilising all the available information and being updated as additional information becomes available e.g. from offspring or siblings;
(ii) the EBV will provide predictors for those animals that do not have a phenotypic record hence increasing selection opportunities and intensity, which again enhances rate of improvement;
(iii) the EBV will be available from the moment of birth for selection (although newborn littermates will have identical EBV) and, in this case, the accuracy (and hence rate of improvement) from using EBV increases by 31% compared to the parental average phenotype;
(iv) the EBV will have been corrected for other fixed effects such as sex and age which bias phenotype as a predictor of genetic merit; and
(v) it may be argued that taking account of a sustainable rate of inbreeding as well as disease prevalence would restrict the selection pressure that can be applied, however this only serves to place a greater emphasis on the accuracy of the selection that does take place.
"Finally with the availability of sequence and dense canine SNP chips, the development of a genomic EBV (an EBV informed by additional information from dense SNP genotypes) would help to distinguish littermates and further increase accuracy, increasing the potential rate of improvement, and might also lead subsequently to scientific benefits through identifying the major QTL. The intention is to make public the EBV for hip score for all KC registered Labrador Retrievers so that all these benefits may be realised."
RETURN TO TOP
Genetics of SM
Genetics of Syringomyelia and Breeding Strategies
to Reduce Occurrence
By SARAH BLOTT, PhD (Quantitative Genetics), MSc (Animal
Breeding)
Genetics Department, Animal Health Trust, UK
Notes for the [UK] Cavalier King Charles Spaniel Clubs Liaison Meeting 18 May 2008
Syringomyelia is believed to be a complex disease, where the disease phenotype results from the effects of several genes plus environmental influences. The phenotype includes not only the affectation status of the individual but also clinical observations and measurements made from MRI scans. In order to determine the genetic basis of the disease two different approaches are being taken. The first uses a population-based approach, where phenotypic measurements and pedigree information are used to estimate the heritability of the disease. This requires that we have accurate phenotypic measurements, including MRI scans, on as much of the population as possible, together with pedigrees so that genetic relationships between individuals can be identified.
Where information exists on other diseases, such as Mitral Valve Disease, this can also be included in the analysis allowing genetic correlations between diseases to be established. It is important to know about correlations, or relationships, between diseases so that any selection strategies take account of the possible influence that selection against one disease may have on other diseases. The second approach to understanding the genetic basis of a disease is to use molecular genetics and gene mapping techniques to try to identify the underlying causative mutations. This approach is also being used to try to identify genes causing both Syringomyelia (SM) and Chiari Malformation (CM) in the Cavalier King Charles Spaniel (CKCS) and other toy breeds such as the Brussels Griffon. It is hoped that this will identify regions of the genome harbouring the genes causing these conditions.
Data collected by Penny Knowler and Clare Rusbridge is currently being used as the basis for the population-based analysis of heritability. Their database contains clinical observations for SM and CM on around 1,400 dogs and MRI scan results for around 700 of these dogs. We have also been given access to the full UK Kennel Club pedigree records for CKCS. This enables us to estimate the heritability of SM and the genetic correlations between SM and measurements made from the MRI scans. The information obtained from this analysis then allows us to derive estimated breeding values (EBVs) for all measured dogs as well as all dogs in the pedigree.
Once the results of the gene mapping studies become available it is hoped to bring this information together with the population analysis to facilitate the calculation of genomic breeding values (geBVs). Early estimates of the heritability of SM suggest it is around 0.7-0.8 (Preliminary estimate which may be subject to later modification) or that 70-80% of the variation between individuals is genetic in origin and about 20-30% is environmental. In the case of SM not much is known about the environmental influences and these may include in-utero or developmental effects. The heritability is sufficiently high, however, that genetic selection against the disease should be very successful. Heritabilities for Chiari Malformation, Cerebellar Herniation and Medullary Kinking are also very high. Genetic correlations between these traits and SM are positive and, interestingly, less than one. This suggests that different genes may be controlling SM and CM and that it will be possible to select against SM even if dogs have the malformation (CM).
One concern that we have at the present is that the estimates of heritability may be biased upwards. This is because the data has been ascertained on the basis of clinical cases. Most dogs will be MRI scanned because of concern that the dog may have SM or because the family or line is known to be afflicted by the condition. It is probably fairly rare that unaffected dogs from clear lines would be MRI scanned. We are taking various approaches to trying to iron out the bias, most based on modifying the statistical analysis, but it would also be beneficial if some dogs identified as unaffected could be MRI scanned. The plan is to then consolidate the estimated breeding values (EBVs) and try to estimate them for the entire UK registered population of CKCS. To help towards this aim we would like to collate the results of MRI scans coming from all clinics that are currently offering scans. We intend to set up a webpage where people can submit information directly and which gives details of where information can be sent by post. We hope to have this in operation in the next few weeks.
Estimated Breeding Values (EBVs) are the best measure available for complex traits of the genetic potential of individuals. The breeding value is the sum of the genetic effects and is the equivalent of an animal’s genotype at all the genes contributing to the disease. The EBVs for SM allow us to go from a dichotomous outcome (affected or unaffected) to an underlying continuous scale of liability. This gives us a much finer grading on which to evaluate dogs, leading to much more accurate selection. As an example, the figure below shows how EBVs compare with the A-F grading based on the MRI scans (gradings proposed by Clare Rusbridge). Grades A-C have more favourable (lower or more negative) EBVs while grades D-F are unfavourable. The gradings, however, do span a range of breeding values and some dogs graded A-C may have EBVs which suggest they can pass on a degree of disease risk to their offspring.
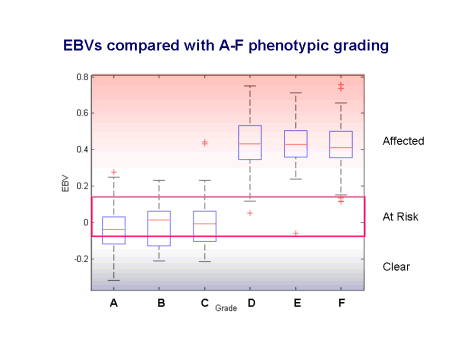 Using
EBVs allows us to distinguish between higher and lower risk dogs in the grading
categories A-C. EBVs can be calculated for most dogs even if they have not been
MRI scanned, as long as they are related to dogs that have been scanned. The
predicted EBV of an individual is half the EBV of its sire plus half the EBV of
its dam. All dogs will have an EBV at birth but the EBV may be modified by the
dog’s subsequent clinical record or MRI scan and by information coming from
other relatives.
Using
EBVs allows us to distinguish between higher and lower risk dogs in the grading
categories A-C. EBVs can be calculated for most dogs even if they have not been
MRI scanned, as long as they are related to dogs that have been scanned. The
predicted EBV of an individual is half the EBV of its sire plus half the EBV of
its dam. All dogs will have an EBV at birth but the EBV may be modified by the
dog’s subsequent clinical record or MRI scan and by information coming from
other relatives.
The EBV becomes more accurate as information on offspring becomes available, because we start to gain insight into which half of the sire and dam genes were actually inherited when we see transmission of the genes to offspring. The accuracy of the EBV increases with numbers of offspring and this may take some time to achieve. In contrast, genomic breeding values (geBVs) provide a high accuracy from birth. By looking directly at the DNA genotypes we can see which genes were inherited from the sire and from the dam, without having to wait for offspring. Genomic breeding values can be used for accurate evaluation at an early stage, before the disease phenotype may be apparent and before a dog is used for breeding.
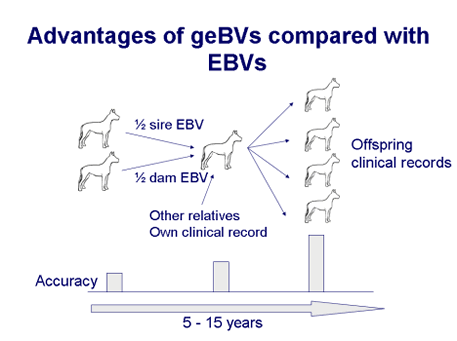 In
addition to selecting away from individual known diseases, such as
syringomyelia, it is important to consider the long-term health of the breed.
Population diversity and maintenance of diversity is important in order to
minimize the risk of future new diseases arising. We want to apply
state-of-the-art genetic selection techniques that use optimal contribution
theory to help avoid unequal representation of individuals in future generations
or ‘genetic bottlenecks’ occurring. This ensures that increases in inbreeding
and loss of diversity are minimized. Our aim is to develop internet-based tools
that allow breeders to have direct access to these state-of-the-art techniques
to help them make optimal selection decisions.
In
addition to selecting away from individual known diseases, such as
syringomyelia, it is important to consider the long-term health of the breed.
Population diversity and maintenance of diversity is important in order to
minimize the risk of future new diseases arising. We want to apply
state-of-the-art genetic selection techniques that use optimal contribution
theory to help avoid unequal representation of individuals in future generations
or ‘genetic bottlenecks’ occurring. This ensures that increases in inbreeding
and loss of diversity are minimized. Our aim is to develop internet-based tools
that allow breeders to have direct access to these state-of-the-art techniques
to help them make optimal selection decisions.
The Cavalier King Charles Spaniel will be the first dog breed in the world for which these techniques will be available. We also plan to explore different breeding strategies, based on computer modelling. This will help us to establish the time-scale over which the disease incidence can be reduced, the range of breeding values that should be used for breeding and the acceptable rate of diversity loss to minimize future disease risk. The immediate next steps in the project are to:
• Widen our data collection effort to include information for as broad a section of the population as we can. We will be setting up a webpage which will give details on how information can be submitted to us.
• Look at ways in which we can get a more accurate or unbiased estimate of the disease incidence.
• Investigate whether SM could be caused by a single gene or whether the multiple gene (polygenic) model fits the data better.
• Include information on Mitral Valve Disease (MVD) with the aim of producing EBVs for MVD.
We are also working towards the longer term aims of:
• Modelling different breeding strategies and identifying the most appropriate strategy.
• Carrying out molecular genetic analysis of SM and CM to identify the underlying genes, in collaboration with the University of Montreal, Clare Rusbridge and Penny Knowler.
• Developing genomic breeding values (geBVs) for SM.
Dr. Blott may be contacted at Genetics Department, Animal Health Trust, , Lanwades Park Kentford, Newmarket, Suffolk CB8 7UU, telephone +44 1638 751000, fax +44 1638 555606, website: www.aht.org.uk
RETURN TO TOP
Research News
April 2025:
UK groups start 5-year syringomyelia screening project of 500
invited cavaliers.
 In
March 2025, the British Veterinary Assn. and the UK Kennel Club
announced the start of the “Cavalier King Charles Spaniel Syringomyelia
Project”, to “better understand syringomyelia within the Cavalier King
Charles Spaniel population”. The project intends to MRI-scan 500
specially invited cavaliers, to collect data to advise dog CKCS owners
on “informed breeding decisions and contribute to the development of
estimated breeding values (EBVs)
for syringomyelia. Cavaliers are to be selected for the project
based upon their age and “their contribution to the Cavalier King
Charles Spaniel Kennel Club registered population”. The project will
focus on dogs born between 2013 and 2018 which have produced at least 3
litters. Invitations to participate will be sent by the UK Kennel Club
to cavalier owners that meet the criteria. Data examiners are to be
Professor Michael Herrtage and Dr. Ruth Dennis. See
this link for more details.
In
March 2025, the British Veterinary Assn. and the UK Kennel Club
announced the start of the “Cavalier King Charles Spaniel Syringomyelia
Project”, to “better understand syringomyelia within the Cavalier King
Charles Spaniel population”. The project intends to MRI-scan 500
specially invited cavaliers, to collect data to advise dog CKCS owners
on “informed breeding decisions and contribute to the development of
estimated breeding values (EBVs)
for syringomyelia. Cavaliers are to be selected for the project
based upon their age and “their contribution to the Cavalier King
Charles Spaniel Kennel Club registered population”. The project will
focus on dogs born between 2013 and 2018 which have produced at least 3
litters. Invitations to participate will be sent by the UK Kennel Club
to cavalier owners that meet the criteria. Data examiners are to be
Professor Michael Herrtage and Dr. Ruth Dennis. See
this link for more details.
December 2024:
Nine genes associated with long-lived cavaliers in the Czech Republic
are identified.
 In a
December 2024 article, genetic researchers (Evžen
Korec [right], Lenka Ungrová, Josef Kalvas, Jirí Hejnar) examined the genetic
makeup of 24 13+ year old cavalier King Charles spaniels, to determine
which genes may be associated with longevity in the breed. All 24 13+
year old cavaliers and 17 younger “reference” CKCSs were owned by CKCS
club members in the Czech Republic. Nine candidate genes were
identified: B3GALNT1, NLRP1 like, PARP14 IQCJ-SCHIP1, COL9A1, COL19A1,
SDHAF4, B3GAT2, and DIRC2. They concluded:
In a
December 2024 article, genetic researchers (Evžen
Korec [right], Lenka Ungrová, Josef Kalvas, Jirí Hejnar) examined the genetic
makeup of 24 13+ year old cavalier King Charles spaniels, to determine
which genes may be associated with longevity in the breed. All 24 13+
year old cavaliers and 17 younger “reference” CKCSs were owned by CKCS
club members in the Czech Republic. Nine candidate genes were
identified: B3GALNT1, NLRP1 like, PARP14 IQCJ-SCHIP1, COL9A1, COL19A1,
SDHAF4, B3GAT2, and DIRC2. They concluded:
“The current knowledge shows that all the genes with SNPs [single-nucleotide polymorphisms] described in this study as associated with longevity in CKCS could directly or indirectly influence health and prolong life. We identified genes associated with common longevity-influencing factors such as cancer, immunity, DNA damage, cellular repair, and oxidative stress. We also found genes that may play a role in the tissue structure and formation. Most importantly, longevity-associated SNPs were found in genes that play a role in heart diseases, which are the major cause of death in the CKCS. We described SNPs in two collagen genes associated with longevity in the CKCS. Collagens were previously described to undergo morphological changes in the dogs affected with mitral valve disease, and changes in their expression in affected CKCS to have a direct effect on longevity. Our results show that the detected longevity-associated SNPs could also serve as potential markers of diseases.”
December 2024:
Dr. Clare Rusbridge calls for cross-breeding cavaliers
and opening their breed registers.
 Dr. Clare Rusbridge
(right), in a
May 2024 article, summarizes the genetic
health plight of the cavalier King Charles spaniel, and calls for the
breed’s cross-breeding and opening of its breed registers, due to “many
health conditions caused by inbreeding.” She states that:
Dr. Clare Rusbridge
(right), in a
May 2024 article, summarizes the genetic
health plight of the cavalier King Charles spaniel, and calls for the
breed’s cross-breeding and opening of its breed registers, due to “many
health conditions caused by inbreeding.” She states that:
“Health testing dogs is not sufficient, breeding is a science, not an amateur endeavour. Cattle breeders already use estimating breeding values. This is the right tool to manage most inherited diseases, dog breeders must do the same. ... Breeding with small genetic populations with closed stud books is not sustainable. Crossbreeding and opening the breed registers is the only way to improve animal welfare and save certain breeds from extinction. If we want some breeds to survive, we have to accept they will need to look different to the modern-day appearance.”
July 2023:
UK study of 30,470 dogs finds mongrels and cross-breeds outlive
purebreds.
 In a
July 2023 article, Portugese researchers Fernando Mata (right)
and Andreia
Mata examined the medical records from UK's Royal Veterinary College of
30,470 dogs (2,406 mongrels, 3,962 crossbreeds, and 24,102 purebreds,
including 1,004 cavalier King Charles spaniels), to determine the
morbidity of dogs based upon inbreeding coefficients. They found that an
increase in a dog's inbreeding coefficient is associated with a lower
lifespan, and that dogs with the longer lifespan were mongrels (mean
12.761 years), followed by cross-bred (11.225 years), and then purebred
(11.086 years). They defined cross-bred as having only one purebred
ancestor. They concluded:
In a
July 2023 article, Portugese researchers Fernando Mata (right)
and Andreia
Mata examined the medical records from UK's Royal Veterinary College of
30,470 dogs (2,406 mongrels, 3,962 crossbreeds, and 24,102 purebreds,
including 1,004 cavalier King Charles spaniels), to determine the
morbidity of dogs based upon inbreeding coefficients. They found that an
increase in a dog's inbreeding coefficient is associated with a lower
lifespan, and that dogs with the longer lifespan were mongrels (mean
12.761 years), followed by cross-bred (11.225 years), and then purebred
(11.086 years). They defined cross-bred as having only one purebred
ancestor. They concluded:
"It was hypothesized that morbidity in dogs may be associated with inbreeding coefficients. The results of this study confirm the hypothesis, showing that survivability is higher in mongrel dogs followed by cross-bred with one of the ancestor only as a pure breed, and for the last pure breed dogs have the highest morbidity levels. Higher morbidity was associated with higher GISID scores, and therefore, higher levels of homozygotic recessive genes in the genomes of the individuals, and inbreeding coefficients should be reduced for better survivability. Future research may be directed to dog breeding, to decrease inbreeding coefficients and control deleterious genes."
April 2022:
Finnish Cavalier King Charles Spaniel Club approves
cross-breeding of CKCS with other breeds to increase genetic diversity
and improve genetic health.
 On
April 23, 2022, the membership of the Finnish Cavalier King Charles
Spaniel Club unanimously approved the start of a croos-breeding program
between purebred CKCSs and one or more other breeds which are free of
the CKCS genetic disorders of early-onset mitral valve disease (MVD),
syringomyelia, and Chiari-like malformation.
On
April 23, 2022, the membership of the Finnish Cavalier King Charles
Spaniel Club unanimously approved the start of a croos-breeding program
between purebred CKCSs and one or more other breeds which are free of
the CKCS genetic disorders of early-onset mitral valve disease (MVD),
syringomyelia, and Chiari-like malformation.
The stated goal of the cross-breeding programl is to improve the breed's health, particularly regarding mitral valve disease (MVD), syringomyelia (SM) and possibly Chiari-like malformation (CM). The Finnish CKCS club has determined that purebred breeding cannot eradicate these conditions or even significantly decrease the number of affected dogs. The club’s plan is to carry out several litters with several breeds, in order to see long-term health results and to ensure sufficient material for further study. No decisions have yet been made sa to which other breeds will be partnered with cavaliers. However, there will be guidelines, such as the partner breed must not show any brachycephalic traits, and its temperament must match that of the typical CKCS. All eventual cross-bred CKCS litters will be bred by registered cavalier breeders under the supervision of both the Finnish Kennel Club and the Finnish CKCS Club. A single cross-bred line will include four generations, the final one being FCI registered as purebred cavalier King Charles spaniel. Completing a single 4-generation line is estimated to take approximately 10 years.
January 2022:
Norway court bans kennel clubs from registering cavalier King Charles spaniels.
 In a lawsuit brought by the Norwegian Society for Protection of Animals,
the Oslo, Norway district court
has ruled today (January 31, 2022) that
registering and breeding cavalier
King Charles spaniels and English bulldogs is illegal under Norway's Animal Welfare Act
Section 25. The three-judge court's decision applies only to Norway's all-breed kennel
club and the two breeds' kennel clubs and six individual breeders. One of the judges is an animal welfare veterinarian, Dr.
Cecilie Marie Mejdell, and another, Dr. Katja Nilsson, is a
geneticist. The ruling follows a 5-day hearing held in November 2021 at
which expert witnesses testified about major health problems in these
two breeds. The ruling leaves open the option of "serious and scientific
cross-breeding" as a "good alternative".
In a lawsuit brought by the Norwegian Society for Protection of Animals,
the Oslo, Norway district court
has ruled today (January 31, 2022) that
registering and breeding cavalier
King Charles spaniels and English bulldogs is illegal under Norway's Animal Welfare Act
Section 25. The three-judge court's decision applies only to Norway's all-breed kennel
club and the two breeds' kennel clubs and six individual breeders. One of the judges is an animal welfare veterinarian, Dr.
Cecilie Marie Mejdell, and another, Dr. Katja Nilsson, is a
geneticist. The ruling follows a 5-day hearing held in November 2021 at
which expert witnesses testified about major health problems in these
two breeds. The ruling leaves open the option of "serious and scientific
cross-breeding" as a "good alternative".
The Norwegian law states that breeding from sick dogs is prohibited, even when the aim is to improve the breed's health. Initiating health programs for breeds with a high burden of disease with the aim of improving the breed's health in a long-term perspective violate the statute. Specifically, Section 25 states:
"§25. Breeding. Breeding must encourage characteristics which give robust animals which function welland have good health. Breeding, including through methods of gene technology, shall not be carried out in such a way that it:a. changes genes in such a way that they influence the animals’ physical or mentalfunctions in a negative way, or passes on such genes,
b. reduces the animals’ ability to practice natural behaviour, or
c. evokes general ethical reactions."
At the November hearing, expert witnesses testified that the current health programs for the English bulldog and the cavalier will lead to dogs borne to a life with substantial suffering for many years to come. In its 63-page opinion, the Oslo court specifically listed Chiari-like malformation, syringomyelia, and mitral valve disease as genetic disorders in the CKCS which are widespread. The court also singled out episodic falling disease and curly coat and dry eye syndrome as being in "overabundance" and "due to hereditary gene mutations". However, those two disorders did not play a role in the court's decision.
In a statement by the Norsk Kennel Klub following the release of the court's decision, their spokesman stated:
"A breeding ban is still not a breed ban, and the consequences of this are great. Irresponsible players will be ready to take over the market, with the production of dogs from breeding that are not subject to any form of control. Then the professional competence, health requirements and information about the health status and history of the breeding animals will disappear, says [Tom Øystein] Martinsen. The breeds in question are very popular. The demand for this type of dog is guaranteed to continue to be high. Although it is forbidden to breed on the two breeds in question, rogue actors with pure profit as motivation will see their average to sell this type of dog. The difference is a lack of overview and control of the breed. As the situation is today, where there is no obligation to ID tag a dog and there is no overview of those who breed outside the NKK system, in principle all unregistered breeding can take place without any kind of follow-up and control. Registered dogs are the solution."
 EDITOR'S
NOTE: There are many loose ends to this court order. First
of all, it applies only to the parties to the lawsuit and not to all
cavalier breeders in Norway. While it restrains the two main kennel
clubs, the all-breed Norsk Kennel Klub and the Norsk Cavalierklubb, and
the three cavalier breeders also included as defendants, it does
not apply to any other cavalier breeders, and especially to the backyard
and puppy mill breeders who do not register their cavaliers with either
of those two kennel clubs. So, while the most responsible breeders will
be restrained from continuing to breed cavaliers, the most irresponsible
ones will pick up the slack and breed more and more CKCSs without any
health testing and sell them to the pet owners who do not care whether
their dogs are registered or not.
EDITOR'S
NOTE: There are many loose ends to this court order. First
of all, it applies only to the parties to the lawsuit and not to all
cavalier breeders in Norway. While it restrains the two main kennel
clubs, the all-breed Norsk Kennel Klub and the Norsk Cavalierklubb, and
the three cavalier breeders also included as defendants, it does
not apply to any other cavalier breeders, and especially to the backyard
and puppy mill breeders who do not register their cavaliers with either
of those two kennel clubs. So, while the most responsible breeders will
be restrained from continuing to breed cavaliers, the most irresponsible
ones will pick up the slack and breed more and more CKCSs without any
health testing and sell them to the pet owners who do not care whether
their dogs are registered or not.
So, this court decision is an attack only upon the responsible breeders of cavaliers, and also a free pass to irresponsible breeders to keep abusing the breed, because (a) it applies only to those who register their dogs with the two Norsk kennel clubs (the all-breed club and the cavalier club), and (b) no court order can prevent sales of cavaliers by puppy mills and backyard breeders, who do not register their litters with the kennel clubs and who sell directly to pet owners, unless a separate lawsuit is filed against each such breeder and the court reaches the same conclusion as this court did, following separate trials for each such breeder. The likelihood of such lawsuits and trials occurring for all breeders is inconceivable.
Secondly, the order is not final and is appealable. We expect that the defendants will appeal it, and until that appeal is concluded, the order will remain unenforceable even against the two kennel clubs and the handful of breeders named in the lawsuit.
The biggest flaw in the judgment is that the ruling is based upon research done on cavaliers from other countries and not dogs registered with the two kennel clubs. The efforts made by the health-conscious, responsible cavalier breeders in the Norsk Cavalierklubb should not be penalized due to studies which have focused on cavaliers from other countries. Any evidence of health problems in cavaliers in the UK or USA or Germany or Holland or elsewhere should have been excluded from the hearing in this case because it would be irrelevant to the health conditions of Norsk cavaliers. There have been ancestors of cavaliers in Norway and other Scandinavian countries since the 1600s. No one can correctly claim that the recent ancestors of all Norsk cavaliers have come from the UK and other countries where research has been conducted. This is a case of mixing the apples with the oranges, the apples being from elsewhere and the oranges from Norway.
But since the order does not prohibit cross-breeding of cavaliers with other breeds, the easiest solution for all Norway cavalier breeders is to mate their breeding stock with King Charles spaniels and then mate those offspring back with purebred cavaliers. Within two generations, we predict they will find they are producing dogs which meet the Norsk Cavalierklubb's breed standard but are not purebred cavaliers and therefore would not be in violation of this court order. That may not be the best solution, but it would send a message back to the powers-that-be in Norway that they are acting from ignorance.
December 2021:
Cavaliers' inbreeding value is nearly twice that of breeding
littermates, a UC-Davis study finds.
 In
a
December 2021 article, University of California at Davis researchers
(Danika Bannasch [right], Thomas Famula, Jonas Donner, Heidi
Anderson, Leena Honkanen, Kevin Batcher, Noa Safra, Sara Thomasy, Robert
Rebhun) examined the DNA records of 49,378 dogs of 227 breeds to
determine the levels of inbreeding and consequences on health. Using
estimated levels of inbreeding (coefficient of inbreeding [F] values),
they found that, overall for the 227 breeds, the mean F value was 0.249.
To put that value in context, they observed that "the breeding of two
first cousins produces F = 0.0625, two half siblings F = 0.125, and two
full siblings or parent-offspring F = 0.25." So, that mean F value of
0.249 is the equivalent of breeding two full siblings or a parent to an
offspring. As for cavaliers, that breed's level of inbreeding was 0.411,
nearly double the mating of two littermates or a parent to offspring
(0.25).
In
a
December 2021 article, University of California at Davis researchers
(Danika Bannasch [right], Thomas Famula, Jonas Donner, Heidi
Anderson, Leena Honkanen, Kevin Batcher, Noa Safra, Sara Thomasy, Robert
Rebhun) examined the DNA records of 49,378 dogs of 227 breeds to
determine the levels of inbreeding and consequences on health. Using
estimated levels of inbreeding (coefficient of inbreeding [F] values),
they found that, overall for the 227 breeds, the mean F value was 0.249.
To put that value in context, they observed that "the breeding of two
first cousins produces F = 0.0625, two half siblings F = 0.125, and two
full siblings or parent-offspring F = 0.25." So, that mean F value of
0.249 is the equivalent of breeding two full siblings or a parent to an
offspring. As for cavaliers, that breed's level of inbreeding was 0.411,
nearly double the mating of two littermates or a parent to offspring
(0.25).
November 2020:
Norway to
decide if breeding of cavalier King Charles spaniels violates Norwegian
law.
 In a
November 2020 press release issued by the Norwegian Society for
Protection of Animals (NSPA), that group has announced that it is suing
the Norwegian Kennel Club, the Norwegian Cavalier King Charles Spaniel
club, and selected breeders to ban the breeding of purebred cavaliers.
The lawsuit is based upon a 2009 Norwegian statute, section 25 of the
Norwegian Animal Welfare Act, which provides that:
In a
November 2020 press release issued by the Norwegian Society for
Protection of Animals (NSPA), that group has announced that it is suing
the Norwegian Kennel Club, the Norwegian Cavalier King Charles Spaniel
club, and selected breeders to ban the breeding of purebred cavaliers.
The lawsuit is based upon a 2009 Norwegian statute, section 25 of the
Norwegian Animal Welfare Act, which provides that:
"§25. Breeding. Breeding must encourage characteristics which give robust animals which function welland have good health. Breeding, including through methods of gene technology, shall not be carried out in such a way that it:a. changes genes in such a way that they influence the animals’ physical or mentalfunctions in a negative way, or passes on such genes,
b. reduces the animals’ ability to practice natural behaviour, or
c. evokes general ethical reactions."
The NSPA's position is that the cavalier breed (among others) is too sick to continue breeding them, and that the lack of genetic diversity makes it impossible to breed "robust and healthy animals" within the remaining population. The NSPA believes that outcrossing of the breed is the only available option that is in accordance with applicable legislation in Norway.
April 2020:
Cavaliers showed breed-specific DNA variations in alanine
transaminase (ALT) levels and stress during exams in gemome-wide
association study.
 In an
April 2020 article, and international team of genome
investigators (Yukihide Momozawa, Anne-Christine Merveille, Géraldine
Battaille, Maria Wiberg, Jørgen Koch, Jakob Lundgren Willesen, Helle
Friis Proschowsky, Vassiliki Gouni, Valérie Chetboul, Laurent Tiret,
Merete Fredholm, Eija H. Seppälä, Hannes Lohi, Michel Georges,
Anne-Sophie Lequarré [right]) studied and compared 40 measurements in a
genome-wide association study (GWAS) of 472 dogs of 8 breeds, including
35 cavalier King Charles spaniels. The measurements included 9
morphometric (body size), 4 urinary, 24 clinical blood tests, and 3
stress responses. The purpose of the study was to investigate the
genetic contribution to individual differences in those 40 measurements.
The cavalier stood out as breed-specific in two categories: Alanine
transaminase (ALT) and stress during physical examination. The ALT level
in blood is used for the diagnosis of liver disease and injury. The
research suggests a genetic effect of a specific single-nucleotide
polymorphism (SNP), namely BICF2P496164, in cavaliers. As for stress
during examinations, the cavalier breed showed the tendency for more
stress due to having the A allele of BICF2P1232291 at chromosome 1. The
researchers concluded:
In an
April 2020 article, and international team of genome
investigators (Yukihide Momozawa, Anne-Christine Merveille, Géraldine
Battaille, Maria Wiberg, Jørgen Koch, Jakob Lundgren Willesen, Helle
Friis Proschowsky, Vassiliki Gouni, Valérie Chetboul, Laurent Tiret,
Merete Fredholm, Eija H. Seppälä, Hannes Lohi, Michel Georges,
Anne-Sophie Lequarré [right]) studied and compared 40 measurements in a
genome-wide association study (GWAS) of 472 dogs of 8 breeds, including
35 cavalier King Charles spaniels. The measurements included 9
morphometric (body size), 4 urinary, 24 clinical blood tests, and 3
stress responses. The purpose of the study was to investigate the
genetic contribution to individual differences in those 40 measurements.
The cavalier stood out as breed-specific in two categories: Alanine
transaminase (ALT) and stress during physical examination. The ALT level
in blood is used for the diagnosis of liver disease and injury. The
research suggests a genetic effect of a specific single-nucleotide
polymorphism (SNP), namely BICF2P496164, in cavaliers. As for stress
during examinations, the cavalier breed showed the tendency for more
stress due to having the A allele of BICF2P1232291 at chromosome 1. The
researchers concluded:
"This study illustrates the importance of performing meta-analysis after breed-specific GWAS to reveal genetic contribution to individual differences in clinical measurements, which would lead to improvement of veterinary medicine."
August 2018:
Purebred study of 23 breeds in Austria, Germany, and Switzerland
finds the CKCS the most homogeneous of all.
 In a
November 2018 article by an international team of geneticists
(Burkhard Berger, Cordula Berger, Josephin Heinrich, Harald
Niederstätter, Werner Hecht, Andreas Hellmann, Udo Rohleder, Uwe
Schleenbecker, Nadja Morf, Ana Freire-Aradas, Dennis McNevin,
Christopher Phillips, Walther Parson [right]), they tested
"short tandem repeat (STR) markers" of the 23 most popular dog breeds in
Austria, Germany, and Switzerland. The testing showed that cavalier King
Charles spaniels (CKCS) had the highest homogeneity among all 23 breeds,
with a STR value of 0.90. The CKCS was followed by the Bernese mountain
dog (0.89), the West Highland white terrier (0.86), and the German
wirehaired pointer (0.86). The breed with the lowest STR marker value
was the Jack Russell terrier (0.29). King Charles spaniels (English toy
spaniels) were not included in the list of 23 breeds studied.
In a
November 2018 article by an international team of geneticists
(Burkhard Berger, Cordula Berger, Josephin Heinrich, Harald
Niederstätter, Werner Hecht, Andreas Hellmann, Udo Rohleder, Uwe
Schleenbecker, Nadja Morf, Ana Freire-Aradas, Dennis McNevin,
Christopher Phillips, Walther Parson [right]), they tested
"short tandem repeat (STR) markers" of the 23 most popular dog breeds in
Austria, Germany, and Switzerland. The testing showed that cavalier King
Charles spaniels (CKCS) had the highest homogeneity among all 23 breeds,
with a STR value of 0.90. The CKCS was followed by the Bernese mountain
dog (0.89), the West Highland white terrier (0.86), and the German
wirehaired pointer (0.86). The breed with the lowest STR marker value
was the Jack Russell terrier (0.29). King Charles spaniels (English toy
spaniels) were not included in the list of 23 breeds studied.
EDITOR'S NOTE: Since it is well known that the modern-day CKCS came into existence in the late 1920s by breeding longer muzzled King Charles spaniels (KCS) -- also known as the English toy spaniels -- the unfortunate thing about this study is that the KCS was not included among the 23 breeds. Fortunately, however, for comparison purposes, both the Jack Russell terrier and its modern-day AKC off-shoot, the Parson Russell* terrier, were included in the 23 breeds on the list.
As for the Jack and Parson Russells, the researchers found they had the closest genetic structure among all of the breeds in the study. That, of course, would be stating the predictably obvious. (See footnote below.) Specifically about the two Russell breeds, they state:"The lowest FST values occurred between Jack Russel [sic] and Parson Russell Terriers, likely indicating a shared genetic history." (FST means the fixation index, which is the measure of differentiation in genetic structure between the two breeds.)It should also be predictable that the CKCS and its immediate ancestor, the KCS, likewise would have a very low FST had they been compared in this study. As it is, without the KCS on the list, the cavalier stands out as being the purest of the breeds among the 23, a totally misleading factoid at best.* The Parson Russell terrier essentially has been the AKC's name for the Jack Russell terrier since 2003 when the AKC recognized the breed. Since then, the two versions of the same breed spun off from each other -- with the Jack Russell terrier remaining a non-AKC working dog with a variety of physical attributes and the Parson Russell becoming an AKC show dog with steadily declining worth as a working breed.
 January 2015:
Research
shows limited genetic divergence between dog breeds in UK and South
Africa. In a
December 2014 report in the Veterinary Record, researchers (K. M.
Summers, R. Ogden, D. N. Clements, A. T. French, A. G. Gow, R. Powell,
B. Corcoran, R. J. Mellanby, and J. P. Schoeman) found very limited genetic
divergence between the dog breeds of the Labrador retriever, German
shepherd dog, and Jack Russell terrier in the geographically isolated
countries of the United Kingdom and South Africa. They attribute this to
similarity in breed standards, importation of dogs, and artificial
insemination. They concluded that:
January 2015:
Research
shows limited genetic divergence between dog breeds in UK and South
Africa. In a
December 2014 report in the Veterinary Record, researchers (K. M.
Summers, R. Ogden, D. N. Clements, A. T. French, A. G. Gow, R. Powell,
B. Corcoran, R. J. Mellanby, and J. P. Schoeman) found very limited genetic
divergence between the dog breeds of the Labrador retriever, German
shepherd dog, and Jack Russell terrier in the geographically isolated
countries of the United Kingdom and South Africa. They attribute this to
similarity in breed standards, importation of dogs, and artificial
insemination. They concluded that:
"An important implication of this study is that genetic diseases detected in a breed are likely to be found in both countries and could be transmitted from founders in either country, exacerbated by the use of artificial insemination, limiting the number of sires."
June
2013:
UK cavalier club and Kennel Club may revise CKCS breed standard for genetic
diversity.
 At the May 26 conference on genetic diversity in the
cavalier King Charles spaniel, sponsored by the UK Cavalier King Charles Spaniel
Club, Belgium's
Cavaliers for Life spokesman Arnold Jacques (right) recommended
that: "We could change the standard of the breed. If we omit the phrases [e.g.,
'White
markings undesirable'], that holds us back from making the combination between parti-colours and whole-colours, this could increase the genetic diversity of
the breed."
At the May 26 conference on genetic diversity in the
cavalier King Charles spaniel, sponsored by the UK Cavalier King Charles Spaniel
Club, Belgium's
Cavaliers for Life spokesman Arnold Jacques (right) recommended
that: "We could change the standard of the breed. If we omit the phrases [e.g.,
'White
markings undesirable'], that holds us back from making the combination between parti-colours and whole-colours, this could increase the genetic diversity of
the breed."
The UK publication, Dog World, reports that, following Mr. Jacques' presentation, the cavalier club proposed to the CKCS regional clubs that changes be made to the breed standard so that references to "white undesirable" are removed from the whole colors, and the words "broken up" in the phrase "black and white well spaced, broken up…" removed from the particolors. The UK Kennel Club's health and breeder services manager, Bill Lambert, who was present at the conference, said that if the majority of cavalier clubs gave their support to the revision of the breed standard, the Kennel Club would be "highly likely" to make the changes. "How much more attractive than outcrossing!" he said.
May 2013: UK Kennel Club announces syringomyelia as a "candidate" for EBVs. The UK Kennel Club, in its 2012 Dog Health Group Annual Report, announced that syringomyelia (along with mitral valve disease) "are candidates for the development of EBVs but require appropriate data collection procedures to be in place." The report goes on:
"A BVA/KC scheme for syringomyelia was launched in 2012 and once enough data has accumulated through the scheme then EBVs for the condition will become a possibility."
July
2012: French researchers
confirm the obvious in trying to control inherited disorders and genetic
diversity in dogs.
 French geneticists Grégoire Leroy
and Xavier Rognon
report in the Veterinary
Journal that:
French geneticists Grégoire Leroy
and Xavier Rognon
report in the Veterinary
Journal that:
"Breeding policies, such as the removal of all carriers from the reproduction pool, may have a range of effects on genetic diversity, depending on the breed and the frequency of deleterious alleles. Limiting the number of offspring per reproducer may also have a positive impact on genetic diversity."
May 2012: Belgium & Dutch cavalier group announces EBV pedigree database. "Cavaliers for Life", an ambitious group of Belgium and Dutch cavalier fanciers, led by Arnold Jacques and Pauline Jordens, has announced that their group's database now contains the pedigrees of all the cavaliers born in the last fifteen years in Holland and Belgium. They stated that, from that data, The University of Leuven in Belgium has carried out a full study of the genetic variation and inbreeding within the breed in Belgium and Holland.
RETURN TO TOP
Related Links
RETURN TO TOP
Veterinary Resources
Coefficients of Inbreeding and Relationship. Sewall Wright. American Naturalist. July 1922;56(645):330-338.
The
things we do to dogs. Simon Wolfensohn. New Scientist. May
1981;90.1253:404-407. Quote: "Man is apt to refer to dog as his best
friend, but it's doubtful whether dog can return the compliment. Our
strange ideas about the appearance of our canine companions have
afflicted many breeds with physical deformities which at best cause the
dogs considerable inconvenience and at worst result in a lifetime of
visits to the vet. Some breeds have developed their own
![]() hereditary
diseases because their short-sighted breeden have been more concerned
with their appearance than their general state of health. Not content
with breeding dogs into peculiar shapes and sizes, we have even taken to
snipping off bits of their anatomy to make them conform to our misguided
ideals." (Watch Dr. Simon Wolfensohn discuss "Pedigree dog health
problems" at Crufts in 1985
on
YouTube.)
hereditary
diseases because their short-sighted breeden have been more concerned
with their appearance than their general state of health. Not content
with breeding dogs into peculiar shapes and sizes, we have even taken to
snipping off bits of their anatomy to make them conform to our misguided
ideals." (Watch Dr. Simon Wolfensohn discuss "Pedigree dog health
problems" at Crufts in 1985
on
YouTube.)
Genetic variability in French dog breeds assessed by pedigree data. G. Leroy, X. Rognon, A. Varlet, C. Joffrin, & E. Verrier. J. Anim. Breed. Genet. (Jan. 2006) 123:1–9. "To conclude, probabilities of gene origin added to computation of inbreeding gave us a lot of information about genetic structure and differences among breeds. Such results can be used to manage the genetic variability of breeds. For the breeds with a large population size, it is possible to limit the number of litters per male: such a rule is already applied in the German Shepherd dog in Germany (Guyader 1989). Moreover breed clubs could support breeding animals, which are little related to the whole population. Such dogs can be detected for instance by the average relatedness of each individual with the whole population (Goyache et al. 2003). For breeds with a small and/or decreasing population size, mating should be made between little related dogs."
Population Structure and Inbreeding From Pedigree Analysis of Purebred Dogs. Federico C. F. Calboli, Jeff Sampson, Neale Fretwell, and David J. Balding. Genetics May 2008;179(1):593-601. Quote: "Dogs are of increasing interest as models for human diseases, and many canine population-association studies are beginning to emerge. The choice of breeds for such studies should be informed by a knowledge of factors such as inbreeding, genetic diversity, and population structure, which are likely to depend on breed-specific selective breeding patterns. To address the lack of such studies we have exploited one of the world's most extensive resources for canine population-genetics studies: the United Kingdom (UK) Kennel Club registration database. We chose 10 representative breeds and analyzed their pedigrees since electronic records were established around 1970, corresponding to about eight generations before present. We find extremely inbred dogs in each breed except the greyhound and estimate an inbreeding effective population size between 40 and 80 for all but 2 breeds. For all but 3 breeds, >90% of unique genetic variants are lost over six generations, indicating a dramatic effect of breeding patterns on genetic diversity. We introduce a novel index Ψ for measuring population structure directly from the pedigree and use it to identify subpopulations in several breeds. As well as informing the design of canine population genetics studies, our results have implications for breeding practices to enhance canine welfare. ... We have found that the loss of genetic diversity is very high, with many breeds losing >90% of singleton variants in just six generations. ... Dog breeds are required to conform to a breed standard, the pursuit of which often involves intensive inbreeding ... This has adverse consequences in terms of loss of genetic variability and high prevalence of recessive genetic disorders. These features make purebred dogs attractive for the study of genetic disorders, but raise concerns about canine welfare. ... On the basis of these results, we concur with Leroy et al. (2006) that remedial action to maintain or increase genetic diversity should now be a high priority in the interests of the health of purebred dogs. Possible remedial action includes limits on the use of popular sires, encouragement of matings across national and continental boundaries, and even the relaxation of breed rules to permit controlled outcrossing."
Inherited defects in pedigree dogs. Part 1: Disorders related to breed standards. Lucy Asher, Gillian Diesel, Jennifer F. Summers, Paul D. McGreevy, Lisa M. Collins. Vet. J. December 2009;182(3):402-411. Quote: "The United Kingdom pedigree-dog industry has faced criticism because certain aspects of dog conformation stipulated in the UK Kennel Club breed standards have a detrimental impact on dog welfare. A review of conformation-related disorders was carried out in the top 50 UK Kennel Club registered breeds using systematic searches of existing information. A novel index to score severity of disorders along a single scale was also developed and used to conduct statistical analyses to determine the factors affecting reported breed predisposition to defects. [Cavalier King Charles spaniel: total disorders: 25.] ... Some large breeds are also reportedly predisposed to valvular disease (e.g. German Shepherd Dog), however, mitral valve disease (severity: 7–12) is more commonly associated with small dog breeds (Borgarelli et al., 2004), particularly the Cavalier King Charles spaniel. The prevalence estimates for mitral valve disease in the Cavalier King Charles spaniel range between 11–45% (Hyun, 2005; Haggstrom et al., 1992; Darke, 1987). ... According to the literature searched, each of the top 50 breeds was found to have at least one aspect of its conformation predisposing it to a disorder; and 84 disorders were either directly or indirectly associated with conformation. The Miniature poodle, Bulldog, Pug and Basset hound had most associations with conformation-related disorders. Further research on prevalence and severity is required to assess the impact of different disorders on the welfare of affected breeds."
Heritability of syringomyelia in Cavalier King Charles spaniels. Tom Lewis, Clare Rusbridge, Penny Knowler, Sarah Blott, John A. Woolliams. Vet.J. March 2010;183(3): 345-347. Quote: "Mixed model analysis of 384 Cavalier King Charles spaniels (CKCS), with a magnetic resonance imaging diagnosis for the presence or absence of a syrinx, in conjunction with the Kennel Club pedigree records of all dogs registered from the mid 1980s to September 2007, revealed a moderately high estimate of heritability of syringomyelia (h2 = 0.37 ± 0.15 standard error) when analysed as a binary trait. Inspection of cases where the disease segregated within families pointed to genes at more than one locus influencing syringomyelia. The availability of estimated breeding values for Kennel Club registered CKCS is a significant step in being able to select against syringomyelia, particularly given the difficulty of ascertaining the disease phenotype."
Localization of Canine Brachycephaly Using an Across Breed Mapping Approach. Danika Bannasch, Amy Young, Jeffrey Myers, Katarina Truvé, Peter Dickinson, Jeffrey Gregg, Ryan Davis, Eric Bongcam-Rudloff, Matthew T. Webster, Kerstin Lindblad-Toh, Niels Pedersen. PLOS One. March 2010. Quote: "The domestic dog, Canis familiaris, exhibits profound phenotypic diversity and is an ideal model organism for the genetic dissection of simple and complex traits. However, some of the most interesting phenotypes are fixed in particular breeds and are therefore less tractable to genetic analysis using classical segregation-based mapping approaches. We implemented an across breed mapping approach using a moderately dense SNP array, a low number of animals and breeds carefully selected for the phenotypes of interest to identify genetic variants responsible for breed-defining characteristics. Using a modest number of affected (10–30) and control (20–60) samples from multiple breeds, the correct chromosomal assignment was identified in a proof of concept experiment using three previously defined loci; hyperuricosuria, white spotting and chondrodysplasia. Genome-wide association was performed in a similar manner for one of the most striking morphological traits in dogs: brachycephalic head type. Although candidate gene approaches based on comparable phenotypes in mice and humans have been utilized for this trait, the causative gene has remained elusive using this method. Samples from nine affected breeds and thirteen control breeds identified strong genome-wide associations for brachycephalic head type on Cfa 1. Two independent datasets identified the same genomic region. Levels of relative heterozygosity in the associated region indicate that it has been subjected to a selective sweep, consistent with it being a breed defining morphological characteristic. Genotyping additional dogs in the region confirmed the association. To date, the genetic structure of dog breeds has primarily been exploited for genome wide association for segregating traits. These results demonstrate that non-segregating traits under strong selection are equally tractable to genetic analysis using small sample numbers."
Optimisation of breeding strategies to reduce the prevalence of inherited disease in pedigree dogs. Lewis, T.W.; Woolliams, J.A.; Blott, S.C. Animal Welfare 19(Supp 1):93-98(6), May 2010. Quote: "One option for improving the welfare of purebred dog breeds is to implement health breeding programmes, which allow selection to be directed against known diseases while controlling the rate of inbreeding to a minimal level in order to maintain the long-term health of the breed. The aim of this study is to evaluate the predicted impact of selection against disease in two breeds: the Cavalier King Charles spaniel (CKCS) .... Heritabilities for mitral valve disease, syringomyelia in the CKCS ... were estimated to be 0.64 (± 0.07), 0.32 (± 0.125) ... respectively, which suggest encouraging selection responses are feasible based upon the estimation of breeding values (EBVs) if monitoring schemes are maintained for these breeds. Although using data from disease databases can introduce problems due to bias, as a result of individuals and families with disease usually being over-represented, the data presented is a step forward in providing information on risk. EBVs will allow breeders to distinguish between potential parents of high and low risk, after removing the influence of life history events. Analysis of current population structure, including numbers of dogs used for breeding, average kinship and average inbreeding provides a basis from which to compare breeding strategies. Predictions can then be made about the number of generations it will take to eradicate disease, the number of affected individuals that will be born during the course of selective breeding and the benefits that can be obtained by using optimisation to constrain inbreeding to a pre-defined sustainable rate.
Mating practices and the dissemination of genetic disorders in domestic animals, based on the example of dog breeding. Leroy G, Baumung R. Anim Genet. February 2011;42(1):66-74. Quote: On the basis of simulations and genealogical data of ten dog breeds, three popular mating practices (popular sire effect, line breeding, close breeding) were investigated along with their effects on the dissemination of genetic disorders. Our results showed that the use of sires in these ten breeds is clearly unbalanced. Depending on the breed, the effective number of sires represented between 33% and 70% of the total number of sires. Mating between close relatives was also found to be quite common, and the percentage of dogs inbred after two generations ranged from 1% to about 8%. A more or less long-term genetic differentiation, linked to line breeding practices, was also emphasized in most breeds. F(IT) index based on gene dropping proved to be efficient in differentiating the effects of the different mating practices, and it ranged from -1.3% to 3.2% when real founders were used to begin a gene dropping process. Simulation results confirmed that the popular sire practice leads to a dissemination of genetic disorders. Under a realistic scenario, regarding the imbalance in the use of sires, the dissemination risk was indeed 4.4 times higher than under random mating conditions. In contrast, line breeding and close breeding practices tend to decrease the risk of the dissemination of genetic disorders.
Getting priorities straight: risk assessment and decision-making in the improvement of inherited disorders in pedigree dogs. Collins LM, Asher L, Summers J, McGreevy P. Vet J. 2011 Aug;189(2):147-54. Quote: "The issue of inherited disorders in pedigree dogs is not a recent phenomenon and reports of suspected genetic defects associated with breeding practices date back to Charles Darwin's time. In recent years, much information on the array of inherited defects has been assimilated and the true extent of the problem has come to light. Historically, the direction of research funding in the field of canine genetic disease has been largely influenced by the potential transferability of findings to human medicine, economic benefit and importance of dogs for working purposes. More recently, the argument for a more canine welfare-orientated approach has been made, targeting research efforts at the alleviation of the most suffering in the greatest number of animals. A method of welfare risk assessment was initially developed as a means of objectively comparing, and thus setting priorities for, different welfare problems. The method has been applied to inherited disorders in pedigree dogs to investigate which disorders have the greatest welfare impact and which breeds are most affected. Work in this field has identified 396 inherited disorders in the top 50 most popular breeds in the UK. This article discusses how the results of welfare risk assessment for inherited disorders can be used to develop strategies for improving the health and welfare of dogs in the long term. A new risk assessment criterion, the Breed-Disorder Welfare Impact Score (BDWIS), which takes into account the proportion of life affected by a disorder, is introduced. A set of health and welfare goals is proposed and strategies for achieving these goals are highlighted, along with potential rate-determining factors at each step."
Genetic diversity, inbreeding and breeding practices in dogs: results from pedigree analyses. Leroy G. Vet J. 2011 Aug;189(2):177-82. Quote: "Pedigree analysis constitutes a classical approach for the study of the evolution of genetic diversity, genetic structure, history and breeding practices within a given breed. As a consequence of selection pressure, management in closed populations and historical bottlenecks, many dog breeds have experienced considerable inbreeding and show (on the basis of a pedigree approach) comparable diversity loss compared to other domestic species. This evolution is linked to breeding practices such as the overuse of popular sires or mating between related animals. The popular sire phenomenon is the most problematic breeding practice, since it has also led to the dissemination of a large number of inherited defects. The practice should be limited by taking measures such as restricting the number of litters (or offspring) per breeding animal."
Inbreeding and genetic diversity in dogs: results from DNA analysis. Wade CM. Vet J. 2011 Aug;189(2):183-8. Quote: "This review assesses evidence from DNA analysis to determine whether there is sufficient genetic diversity within breeds to ensure that populations are sustainable in the absence of cross breeding and to determine whether genetic diversity is declining. On average, dog breeds currently retain approximately 87% of the available domestic canine genetic diversity. Requirements that breeding stock must be 'clear' for all genetic disorders may firstly place undue genetic pressure on animals tested as being 'clear' of known genetic disorders, secondly may contribute to loss of diversity and thirdly may result in the dissemination of new recessive disorders for which no genetic tests are available. Global exchange of genetic material may hasten the loss of alleles and this practice should be discussed in relation to the current effective population size of a breed and its expected future popularity. Genomic data do not always support the results from pedigree analysis and possible reasons for this are discussed."
Is gene loss in pedigree dogs surprisingly rapid? James JW. Vet J. August 2011;189(2):211-3. Quote: Factors affecting the probabilities of gene loss are discussed, with particular attention given to population expansion, sex ratio and inbreeding. Much of the variation in gene survival probabilities among breeds can be explained by differences in expansion rate, sex ratio and family size, with little or no influence of average inbreeding and population size.
Researcher responsibilities and genetic counseling for pure-bred dog populations. Bell Jerold S. Vet J. 2011 Aug;189(2):234-5. Quote: "Breeders of dogs have ethical responsibilities regarding the testing and management of genetic disease. Molecular genetics researchers have their own responsibilities, highlighted in this article. Laboratories offering commercial genetic testing should have proper sample identification and quality control, official test result certificates, clear explanations of test results and reasonably priced testing fees. Providing test results to a publicly-accessible genetic health registry allows breeders and the public to search for health-tested parents to reduce the risk of producing or purchasing affected offspring. Counseling on the testing and elimination of defective genes must consider the effects of genetic selection on the population. Recommendations to breed quality carriers to normal-testing dogs and replacing them with quality normal-testing offspring will help to preserve breeding lines and breed genetic diversity."
Genetic Evaluation of Hip Score in UK Labrador Retrievers. Thomas W. Lewis, Sarah C. Blott, John A. Woolliams. PLoS ONE 5(10): e12797. . Quote: "The presented results have demonstrated that the availability of EBV through routine evaluations of the hip score data would hasten progress in alleviating the problem of hip dysplasia via increases in selective accuracy compared to selection based on phenotype alone. However the benefits of EBV extend beyond the simple comparisons of accuracy for a recently scored dog: (i) the EBV for an individual, unlike its phenotypic score, will further increase in accuracy over time by utilising all the available information and being updated as additional information becomes available e.g. from offspring or siblings; (ii) the EBV will provide predictors for those animals that do not have a phenotypic record hence increasing selection opportunities and intensity, which again enhances rate of improvement; (iii) the EBV will be available from the moment of birth for selection (although newborn littermates will have identical EBV) and, in this case, the accuracy (and hence rate of improvement) from using EBV increases by 31% compared to the parental average phenotype; (iv) the EBV will have been corrected for other fixed effects such as sex and age which bias phenotype as a predictor of genetic merit; and (v) it may be argued that taking account of a sustainable rate of inbreeding as well as disease prevalence would restrict the selection pressure that can be applied, however this only serves to place a greater emphasis on the accuracy of the selection that does take place. Finally with the availability of sequence [24] and dense canine SNP chips, the development of a genomic EBV (an EBV informed by additional information from dense SNP genotypes [25]) would help to distinguish littermates and further increase accuracy, increasing the potential rate of improvement, and might also lead subsequently to scientific benefits through identifying the major QTL. The intention is to make public the EBV for hip score for all KC registered Labrador Retrievers so that all these benefits may be realised. "
Identification of Genomic Regions Associated with Phenotypic Variation between Dog Breeds using Selection Mapping. Amaury Vaysse, Abhirami Ratnakumar, Thomas Derrien, Erik Axelsson, Gerli Rosengren Pielberg, Snaevar Sigurdsson, Tove Fall, Eija H. Seppälä, Mark S. T. Hansen, Cindy T. Lawley, Elinor K. Karlsson, The LUPA Consortium, Danika Bannasch, Carles Vilà, Hannes Lohi, Francis Galibert, Merete Fredholm, Jens Häggström, Åke Hedhammar, Catherine André, Kerstin Lindblad-Toh, Christophe Hitte, Matthew T. Webster. October 2011. PLOS Genetics. Quote: The extraordinary phenotypic diversity of dog breeds has been sculpted by a unique population history accompanied by selection for novel and desirable traits. Here we perform a comprehensive analysis using multiple test statistics to identify regions under selection in 509 dogs from 46 diverse breeds using a newly developed high-density genotyping array consisting of >170,000 evenly spaced SNPs. We first identify 44 genomic regions exhibiting extreme differentiation across multiple breeds. Genetic variation in these regions correlates with variation in several phenotypic traits that vary between breeds, and we identify novel associations with both morphological and behavioral traits. We next scan the genome for signatures of selective sweeps in single breeds, characterized by long regions of reduced heterozygosity and fixation of extended haplotypes. These scans identify hundreds of regions, including 22 blocks of homozygosity longer than one megabase in certain breeds. Candidate selection loci are strongly enriched for developmental genes. We chose one highly differentiated region, associated with body size and ear morphology, and characterized it using high-throughput sequencing to provide a list of variants that may directly affect these traits. This study provides a catalogue of genomic regions showing extreme reduction in genetic variation or population differentiation in dogs, including many linked to phenotypic variation. The many blocks of reduced haplotype diversity observed across the genome in dog breeds are the result of both selection and genetic drift, but extended blocks of homozygosity on a megabase scale appear to be best explained by selection. Further elucidation of the variants under selection will help to uncover the genetic basis of complex traits and disease.
Empowering international canine inherited disorder management. Bethany J. Wilson and Claire M. Wade. Mammalian Genome. October 2011. Quote: For multifactorial traits, high-quality genetic evaluations are typically conducted by scoring one or more appropriate phenotypes and calculating Estimated Breeding Values (EBVs) for the disorder ... An evaluated animal’s EBV represents the superiority of the animal’s genes that affect the breeding objective relative to the complement of genes of the ‘‘average’’ animal in the breed or in a cohort. All available information about the animal’s value as a breeding animal is combined, with appropriate statistical weighting techniques, into the EBV. When considering disease phenotypes, the information from the candidate itself, its relatives, marker genotypes related to the phenotype from either the individual of concern or its relatives, and phenotypes or marker genotypes for genetically correlated traits (traits controlled by common genetic loci) can be incorporated into the evaluation process. The quality of the information provided by each information source in consideration of the breeding objective affects the importance accorded this information in the final EBV calculation. ... Because in dog populations relatively few progeny are derived from any given parent, it may not be possible to evaluate entirely genomic EBVs for dogs with great accuracy ... and so the collection, storage, cleaning, and processing of phenotype and pedigree information will remain necessary for the foreseeable future. ... There is considerable current research activity toward understanding the genes responsible for single-locus genetic disorders and the genes that contribute in a large way to complex genetic disorders. This research is vital for understanding the aetiology and pathogenesis of these disorders, providing a foundation for future development of treatments and therapies, understanding the diseases as a potential model for analogous human disease and the development of genetic tests for these genes (or markers of these genes) to potentially aid control through selective breeding. Generally, it is the last of these aims, genetic tests, which has the greatest potential for immediate improvement of canine welfare.
Assessing the impact of breeding strategies on inherited disorders and genetic diversity in dogs. Grégoire Leroy, Xavier Rognon. Vet.J. July 2012. Quote: "In the context of management of genetic diversity and control of genetic disorders within dog breeds, a method is proposed for assessing the impact of different breeding strategies that takes into account the genealogical information specific to a given breed. Two types of strategies were investigated: (1) eradication of an identified monogenic recessive disorder, taking into account three different mating limitations and various initial allele frequencies; and (2) control of the population sire effect by limiting the number of offspring per reproducer. The method was tested on four dog breeds: Braque Saint Germain, Berger des Pyrénées, Coton de Tulear and Epagneul Breton. Breeding policies, such as the removal of all carriers from the reproduction pool, may have a range of effects on genetic diversity, depending on the breed and the frequency of deleterious alleles. Limiting the number of offspring per reproducer may also have a positive impact on genetic diversity."
So many doggone traits: mapping genetics of multiple phenotypes in the domestic dog. Maud Rimbault and Elaine A. Ostrander. Human Molecular Genetics. August 2012. Quote: "The worldwide dog population is fragmented into >350 domestic breeds. Breeds share a common ancestor, the gray wolf. The intense artificial selection imposed by humans to develop breeds with particular behaviors and phenotypic traits has occurred primarily in the last 200–300 years. As a result, the number of genes controlling the major differences in body size, leg length, head shape, etc. that define each dog is small, and genetically tractable. This is in comparison to many human complex traits where small amounts of variance are controlled by literally hundreds of genes. We have been interested in disentangling the genetic mechanisms controlling breed-defining morphological traits in the domestic dog. The structure of the dog population, comprised large numbers of pure breeding populations, makes this task surprisingly doable. In this review, we summarize recent work on the genetics of body size, leg length and skull shape, while setting the stage for tackling other traits. It is our expectation that these results will contribute to a better understanding of mammalian developmental processes overall."
Variation of BMP3 Contributes to Dog Breed Skull Diversity. Jeffrey J. Schoenebeck, Sarah A. Hutchinson, Alexandra Byers, Holly C. Beale, Blake Carrington, Daniel L. Faden, Maud Rimbault, Brennan Decker, Jeffrey M. Kidd, Raman Sood, Adam R. Boyko, John W. Fondon III, Robert K. Wayne, Carlos D. Bustamante, Brian Ciruna, Elaine A. Ostrander. PLOS Genetics. August 2012. Quote: "Since the beginnings of domestication, the craniofacial architecture of the domestic dog has morphed and radiated to human whims. By beginning to define the genetic underpinnings of breed skull shapes, we can elucidate mechanisms of morphological diversification while presenting a framework for understanding human cephalic disorders. Using intrabreed association mapping with museum specimen measurements, we show that skull shape is regulated by at least five quantitative trait loci (QTLs). Our detailed analysis using whole-genome sequencing uncovers a missense mutation in BMP3. Validation studies in zebrafish show that Bmp3 function in cranial development is ancient. Our study reveals the causal variant for a canine QTL contributing to a major morphologic trait."
Do dog owners perceive the clinical signs related to conformational inherited disorders as ‘normal’ for the breed? A potential constraint to improving canine welfare. (Owner recognition of breathing disorders in brachycephalic dogs). RMA Packer, A Hendricks and CC Burn. Animal Welfare. 2012;21(S1):81-93. Quote: "Selection for brachycephalic (foreshortened muzzle) phenotypes in dogs is a major risk factor for brachycephalic obstructive airway syndrome (BOAS). Clinical signs include respiratory distress, exercise intolerance, upper respiratory noise and collapse. Efforts to combat BOAS may be constrained by a perception that it is ‘normal’ in brachycephalic dogs. This study aimed to quantify ownerperception of the clinical signs of BOAS as a veterinary problem. A questionnaire-based study was carried out over five months on the owners of dogs referred to the Queen Mother Hospital for Animals (QMHA) for all clinical services, except for Emergency and Critical Care. Owners reported the frequency of respiratory difficulty and characteristics of respiratory noise in their dogs in four scenarios, summarised as an ‘owner-reported breathing’ (ORB) score. Owners then reported whether their dog currently has, or has a history of, ‘breathing problems’. Dogs (n = 285) representing 68 breeds were included, 31 of which were classed as ‘affected’ by BOAS either following diagnostics, or by fitting case criteria based on their ORB score, skull morphology and presence of stenotic nares. The median ORB score given by affected dogs’ owners was 20/40 (range 8–30). Over half (58%) of owners of affected dogs reported that their dog did not have a breathing problem. This marked disparity between owners’ reports of frequent, severe clinical signs and their perceived lack of a ‘breathing problem’ in their dogs is of concern. Without appreciation of the welfare implications of BOAS, affected but undiagnosed dogs may be negatively affected indefinitely through lack of treatment. Furthermore, affected dogs may continue to be selected in breeding programmes, perpetuating this disorder."
Breed Health Improvement Strategy: a Step-by-step Guide. Ian Seath. The Kennel Club. October 2012.
The effects of dog breed development on genetic diversity and the relative influences of performance and conformation breeding. N. Pedersen, H. Liu, G. Theilen, B. Sacks. Anim.Breeding&Genetics. December 2012. Quote: "Genetic diversity was compared among eight dog breeds selected primarily for conformation (Standard Poodle, Italian Greyhound and show English Setter), conformation and performance (Brittany), predominantly performance (German Shorthaired and Wirehaired Pointers) or solely performance (field English Setter and Red Setter). Modern village dogs, which better reflect ancestral genetic diversity, were used as the standard. Four to seven maternal and one to two Y haplotypes were found per breed, with one usually dominant. Diversity of maternal haplotypes was greatest in village dogs, intermediate in performance breeds and lowest in conformation breeds. Maternal haplotype sharing occurred across all breeds, while Y haplotypes were more breed specific. Almost all paternal haplotypes were identified among village dogs, with the exception of the dominant Y haplotype in Brittanys, which has not been identified heretofore. The highest heterozygosity based on 24 autosomal microsatellites was found in village dogs and the lowest in conformation (show) breeds. Principal coordinate analysis indicated that conformation-type breeds were distinct from breeds heavily used for performance, the latter clustering more closely with village dogs. The Brittany, a well-established dual show and field breed, was also genetically intermediate between the conformation and performance breeds. The number of DLA-DRB1 alleles varied from 3 to 10 per breed with extensive sharing. SNPs across the wider DLA region were more frequently homozygous in all pure breeds than in village dogs. Compared with their village dog relatives, all modern breed dogs exhibit reduced genetic diversity. Genetic diversity was even more reduced among breeds under selection for show/conformation."
Comparative analyses of genetic trends and prospects for selection against hip and elbow dysplasia in 15 UK dog breeds. Lewis TW, Blott SC, Woolliams JA. BMC Genet. March 2013;14:16. Quote: "Background: Hip dysplasia remains one of the most serious hereditary diseases occurring in dogs despite long-standing evaluation schemes designed to aid selection for healthy joints. Many researchers have recommended the use of estimated breeding values (EBV) to improve the rate of genetic progress from selection against hip and elbow dysplasia (another common developmental orthopaedic disorder), but few have empirically quantified the benefits of their use. This study aimed to both determine recent genetic trends in hip and elbow dysplasia, and evaluate the potential improvements in response to selection that publication of EBV for such diseases would provide, across a wide range of pure-bred dog breeds. Results: The genetic trend with respect to hip and elbow condition due to phenotypic selection had improved in all breeds, except the Siberian Husky. However, derived selection intensities are extremely weak, equivalent to excluding less than a maximum of 18% of the highest risk animals from breeding. EBV for hip and elbow score were predicted to be on average between 1.16 and 1.34 times more accurate than selection on individual or both parental phenotypes. Additionally, compared to the proportion of juvenile animals with both parental phenotypes, the proportion with EBV of a greater accuracy than selection on such phenotypes increased by up to 3-fold for hip score and up to 13-fold for elbow score. Conclusions: EBV are shown to be both more accurate and abundant than phenotype, providing more reliable information on the genetic risk of disease for a greater proportion of the population. Because the accuracy of selection is directly related to genetic progress, use of EBV can be expected to benefit selection for the improvement of canine health and welfare. Public availability of EBV for hip score for the fifteen breeds included in this study will provide information on the genetic risk of disease in nearly a third of all dogs annually registered by the UK Kennel Club, with in excess of a quarter having an EBV for elbow score as well."
Estimated Breeding Values for Canine Hip Dysplasia Radiographic Traits in a Cohort of Australian German Shepherd Dogs. Bethany J. Wilson, Frank W. Nicholas, John W. James, Claire M. Wade, and Peter C. Thomson. PLoS One. October 2013;8(10):e77470. Quote: "Canine hip dysplasia (CHD) is a serious and common musculoskeletal disease of pedigree dogs and therefore represents both an important welfare concern and an imperative breeding priority. The typical heritability estimates for radiographic CHD traits suggest that the accuracy of breeding dog selection could be substantially improved by the use of estimated breeding values (EBVs) in place of selection based on phenotypes of individuals. The British Veterinary Association/Kennel Club scoring method is a complex measure composed of nine bilateral ordinal traits, intended to evaluate both early and late dysplastic changes. However, the ordinal nature of the traits may represent a technical challenge for calculation of EBVs using linear methods. The purpose of the current study was to calculate EBVs of British Veterinary Association/Kennel Club traits in the Australian population of German Shepherd Dogs, using linear (both as individual traits and a summed phenotype), binary and ordinal methods to determine the optimal method for EBV calculation. Ordinal EBVs correlated well with linear EBVs (r=0.90–0.99) and somewhat well with EBVs for the sum of the individual traits (r=0.58–0.92). Correlation of ordinal and binary EBVs varied widely (r=0.24–0.99) depending on the trait and cut-point considered. The ordinal EBVs have increased accuracy (0.48–0.69) of selection compared with accuracies from individual phenotype-based selection (0.40–0.52). Despite the high correlations between linear and ordinal EBVs, the underlying relationship between EBVs calculated by the two methods was not always linear, leading us to suggest that ordinal models should be used wherever possible. As the population of German Shepherd Dogs which was studied was purportedly under selection for the traits studied, we examined the EBVs for evidence of a genetic trend in these traits and found substantial genetic improvement over time. This study suggests the use of ordinal EBVs could increase the rate of genetic improvement in this population."
Longevity and mortality of owned dogs in England. D G O'Neill, D B Church, P D McGreevy, P C Thomson, D C Brodbelt. Vet. J. December 2013;189(3):638-643. Quote: Average lifespan of popular dog breeds ... Cavalier King Charles Spaniel 9.9 years.
Limited genetic divergence between dog breeds from geographically isolated countries. K. M. Summers, R. Ogden, D. N. Clements, A. T. French, A. G. Gow, R. Powell, B. Corcoran, R. J. Mellanby, J. P. Schoeman. Vet. Record. December 2014;175(22). Quote: "Genetic isolation in a population of UK dogs (Mellanby and others 2013) has been demonstrated previously. ... The authors were interested to assess whether dog breeds in another country had similar levels of genetic isolation. ... Genotypes using 15 microsatellite markers were established for 14 labrador retrievers, 26 German shepherd dogs and 35 Jack Russell terriers from South Africa, using the previously published protocol (Ogden and others 2011, Mellanby and others 2013). Calculations of heterozygosity and relative genetic distance were performed ... This analysis showed that within a breed the dogs were genetically very similar regardless of the country. Jack Russell terriers showed equal contributions from different subpopulations, whereas labrador retrievers and German shepherd dogs each showed 90 per cent contribution from a single subpopulation. Jack Russell terriers had very little contribution from either of the subpopulations predominant in the labrador retrievers or German shepherd dogs, as might be expected given the very different phenotype and ancestry of these dogs. The admixture of subpopulations within a breed was the same regardless of country, showing that the breeds have not diverged greatly. ... This analysis shows that the assignment of dogs to pedigree classes on the basis of genotype is robust across the two countries and there is little evidence for genetic drift within breeds, reflecting the similarity of the breed standards between the two countries. This may be maintained by the import of dogs from other countries and the exchange of semen for artificial insemination. ... Thus, the geographical isolation of the two countries has not apparently led to genetic divergence within the breeds examined, suggesting that there is minimal reproductive isolation and considerable genetic exchange. Consequently, an important implication of this study is that genetic diseases detected in a breed (Asher and others 2009, Summers and others 2010) are likely to be found in both countries and could be transmitted from founders in either country, exacerbated by the use of artificial insemination, limiting the number of sires."
The challenges of pedigree dog health: approaches to combating inherited disease. Lindsay L Farrell, Jeffrey J Schoenebeck, Pamela Wiener, Dylan N Clements, Kim M Summers. Canine Genetics & Epidemiology. February 2015;2(3):1-14. Quote: "The issue of inherited disorders and poor health in pedigree dogs has been widely discussed in recent years. With the advent of genome-wide sequencing technologies and the increasing development of new diagnostic DNA disease tests, the full extent and prevalence of inherited disorders in pedigree dogs is now being realized. In this review we discuss the challenges facing pedigree dog breeds: the common pitfalls and problems associated with combating single gene mediated disorders, phenotypic selection on complex disorders, and ways of managing genetic diversity. ... The Cavalier King Charles Spaniel (CKCS) breed is susceptible to 25 inherited disorders, the most common of which is early-onset myxomatous mitral valve disease (MMVD). In a 2004 survey, 42.8% of all UK CKCS died due to cardiac causes and there is increasing evidence that CKCS mitral valve disease is genetic in origin, with a heritability of between 0.33 and 0.67. ... Breeding strategies incorporating screening schemes have been shown to be successful in significantly reducing the prevalence of an inherited disorder and improving the overall health in certain breeds. However, with 215 breeds officially recognized by the Kennel Club in the United Kingdom and 396 inherited disorders currently identified, many breeds have reached the point at which successfully breeding away from susceptible individuals at a population-wide scale will require new genomic selection strategies in combination with currently available breeding schemes. Whilst DNA-based tests identifying disease causing mutation(s) remain the most informative and effective approach for single gene disorder disease management, they must be used along with current screening schemes, genomic selection, and pedigree information in breeding programs in the effort to maintain genetic diversity while also significantly reducing the number of inherited disorders in pedigree dogs."
Trends in genetic diversity for all Kennel Club registered pedigree dog breeds. T. W. Lewis, B.M. Abhayaratne, S. C. Blott. Canine Genetics and Epidemiology. September 2015;2:13. Quote: "Background: Inbreeding is inevitable in closed populations with a finite number of ancestors and where there is selection. Therefore, management of the rate of inbreeding at sustainable levels is required to avoid the associated detrimental effects of inbreeding. Studies have shown some pedigree dog breeds to have high levels of inbreeding and a high burden of inherited disease unrelated to selection objectives, implying loss of genetic diversity may be a particular problem for pedigree dogs. Pedigree analysis of all 215 breeds currently recognised by the UK Kennel Club over the period 1980–2014 was undertaken to ascertain parameters describing the rate of loss of genetic diversity due to inbreeding, and the presence of any general trend across all breeds. Results: The trend over all breeds was for the rate of inbreeding to be highest in the 1980s and 1990s, tending to decline after 2000. The trend was comparable in very common and rarer breeds, although was more pronounced in rarer breeds. Rates of inbreeding over the entire period 1980–2014 were not correlated with census population size. The existence of popular sires was apparent in all breeds. Conclusion: The trends detected over 1980–2014 imply an initial excessive loss of genetic diversity which has latterly fallen to sustainable levels, even with modest restoration in some cases. The theory of genetic contributions, which demonstrates the fundamental relationship of inbreeding and selection, implies that popular sires are the major contributor to high rate of inbreeding.
Evaluating the performance of selection scans to detect selective sweeps in domestic dogs. Florencia Schlamp, Julian van der Made, Rebecca Stambler, Lewis Chesebrough, Adam R Boyko, Philipp W Messer. BioRxiv. October 2015. Quote: "Selective breeding of dogs has resulted in repeated artificial selection on breed-specific morphological phenotypes. A number of quantitative trait loci associated with these phenotypes have been identified in genetic mapping studies. We analyzed the population genomic signatures observed around the causal mutations for 12 of these loci in 25 dog breeds, for which we genotyped 25 individuals in each breed. By measuring the population frequencies of the causal mutations in each breed, we identified those breeds in which specific mutations most likely experienced positive selection. These instances were then used as positive controls for assessing the performance of popular statistics to detect selection from population genomic data. We found that artificial selection during dog domestication has left characteristic signatures in the haplotype and nucleotide polymorphism patterns around selected loci that can be detected in the genotype data from a single population sample. However, the sensitivity and accuracy at which such signatures were detected varied widely between loci, the particular statistic used, and the choice of analysis parameters. We observed examples of both hard and soft selective sweeps and detected strong selective events that removed genetic diversity almost entirely over regions >10 Mbp. Our study demonstrates the power and limitations of selection scans in populations with high levels of linkage disequilibrium due to severe founder effects and recent population bottlenecks."
Serum Biochemical Phenotypes in the Domestic Dog. Yu-Mei Chang, Erin Hadox, Balazs Szladovits, Oliver A. Garden. PlosOne. February 2016. Quote: "The serum or plasma biochemical profile is essential in the diagnosis and monitoring of systemic disease in veterinary medicine, but current reference intervals typically take no account of breed-specific differences. Breed-specific hematological phenotypes have been documented in the domestic dog, but little has been published on serum biochemical phenotypes in this species. Serum biochemical profiles of dogs in which all measurements fell within the existing reference intervals were retrieved from a large veterinary database. Serum biochemical profiles from 3045 dogs were retrieved, of which 1495 had an accompanying normal glucose concentration. Sixty pure breeds plus a mixed breed control group were represented by at least 10 individuals. All analytes, except for sodium, chloride and glucose, showed variation with age. Total protein, globulin, potassium, chloride, creatinine, cholesterol, total bilirubin, ALT, CK, amylase, and lipase varied between sexes. Neutering status significantly impacted all analytes except albumin, sodium, calcium, urea, and glucose. Principal component analysis of serum biochemical data revealed 36 pure breeds with distinctive phenotypes. Furthermore, comparative analysis identified 23 breeds with significant differences from the mixed breed group in all biochemical analytes except urea and glucose. Eighteen breeds were identified by both principal component and comparative analysis. Tentative reference intervals were generated for breeds with a distinctive phenotype identified by comparative analysis and represented by at least 120 individuals [including 174 cavalier King Charles spaniels]. This is the first large-scale analysis of breed-specific serum biochemical phenotypes in the domestic dog and highlights potential genetic components of biochemical traits in this species."
Dog breed affiliation with a forensically validated canine STR set. Burkhard Berger, Cordula Berger, Josephin Heinrich, Harald Niederstätter, Werner Hecht, Andreas Hellmann, Udo Rohleder, Uwe Schleenbecker, Nadja Morf, Ana Freire-Aradas, Dennis McNevin, Christopher Phillips, Walther Parson. Forensic Sci. Int'l: Genetics. November 2-18;37:126-134. Quote: We tested a panel of 13 highly polymorphic canine short tandem repeat (STR) markers for dog breed assignment using 392 dog samples from the 23 most popular breeds in Austria, Germany, and Switzerland. This STR panel had originally been selected for canine identification. The dog breeds sampled in this study featured a population frequency ≥1% and accounted for nearly 57% of the entire pedigree dog population in these three countries. Breed selection was based on a survey comprising records for nearly 1.9 million purebred dogs belonging to more than 500 different breeds. To derive breed membership from STR genotypes, a range of algorithms were used. These methods included discriminant analysis of principal components (DAPC), STRUCTURE, GeneClass2, and the adegenet package for R. STRUCTURE analyses suggested 21 distinct genetic clusters. Differentiation between most breeds was clearly discernable. Fourteen of 23 breeds (61%) exhibited maximum mean cluster membership proportions of more than 0.70 with a highest value of 0.90 found for Cavalier King Charles Spaniels. Dogs of only 6 breeds (26%) failed to consistently show only one major cluster. The DAPC method yielded the best assignment results in all 23 declared breeds with 97.5% assignment success. The frequency-based assignment test also provided a high success rate of 87%. These results indicate the potential viability of dog breed prediction using a well-established and sensitive set of 13 canine STR markers intended for forensic routine use.
Longevity and mortality in Kennel Club registered dog breeds in the UK in 2014. T. W. Lewis, B. M. Wiles, A. M. Llewellyn-Zaidi, K. M. Evans, D. G. O’Neill. Canine Genetics & Epidem. October 2018;5:10. Quote: Background: The domestic dog is one of the most diverse mammalian species, exhibiting wide variations in morphology, behaviour and morbidity across breeds. Therefore, it is not unexpected that breeds should also exhibit variation in mortality and longevity. While shorter longevity per se may not necessarily be a welfare issue, a generally foreshortened lifespan in a breed that is accompanied by a high prevalence of a particular cause of death may reveal potentially serious welfare concerns and highlight scope to improve breed welfare. Survey data gathered directly from owners offer useful insights into canine longevity and mortality that can support the overall evidence base for welfare reforms within breeds. Results: Mortality data on 5663 deceased dogs [222 cavalier King Charles spaniels] registered with the UK Kennel Club were collected from an owner-based survey. The most commonly reported causes of death were old age (13.8%), unspecified cancer (8.7%) and heart failure (4.9%) [CKCSs: 19.82%] with 5.1% of deaths reported as unknown cause. Overall median age at death was 10.33 years [CKCS: 9.75 years](interquartile range: 7.17–12.83 years). Breeds varied widely in median longevity overall from the West Highland Terrier (12.71 years) to the Dobermann Pinscher (7.67 years). There was also wide variation in the prevalence of some common causes of death among breeds, and in median longevity across the causes of death. ... Many of these associations concur with previous reports in these breeds. For example, our study determined a higher proportional mortality from cardiac disorders in the Cavalier King Charles Spaniel (WBPM of 19.82% for heart failure and 10.81% for cardiomyopathy compared to the OPM of 4.89% and 2.93% respectively) which is concordant with previous reports that cardiac conditions were the most common cause of death in this breed. ... Conclusion: Substantial variation in the median lifespan and the prominent causes of death exists across breeds. This study has identified some breeds with both a low median lifespan and also a high proportional mortality for one or more specific causes of death that should be considered as both potential welfare concerns as well as opportunities for improvement.
Genome wide association study of 40 clinical measurements in eight dog breeds. Yukihide Momozawa, Anne-Christine Merveille, Géraldine Battaille, Maria Wiberg, Jørgen Koch, Jakob Lundgren Willesen, Helle Friis Proschowsky, Vassiliki Gouni, Valérie Chetboul, Laurent Tiret, Merete Fredholm, Eija H. Seppälä, Hannes Lohi, Michel Georges, Anne-Sophie Lequarré. Sci. Rep. April 2020;10:6520; doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-63457-y. Quote: The domestic dog represents an ideal model for identifying susceptibility genes, many of which are shared with humans. In this study, we investigated the genetic contribution to individual differences in 40 clinically important measurements [9 morphometric, 4 urinary, 24 clinical blood, and 3 stress responses] by a genome-wide association study (GWAS) in a multinational cohort of 472 healthy dogs from eight breeds ... (Belgian Shepherd, Cavalier King Charles Spaniel [35 Swedish male dogs], Dachshund, Doberman, Finnish Lapphund, German Shepherd, Labrador Retriever, and Newfoundland) from five countries (Belgium, Denmark, Finland, France, and Sweden). ... Meta-analysis using the binary effects model after breed-specific GWAS, identified 13 genome-wide significant associations, three of them showed experimental-wide significant associations. We detected a signal at chromosome 13 for the serum concentration of alanine aminotransferase (ALT) in which we detected four breed-specific signals. A large proportion of the variance of ALT was explained by this locus. Similarly, a single SNP was also responsible for a large proportion of the variance for other measurements such as fructosamine, stress during physical exam, glucose, and morphometric measurements. The genetic contribution of single variant was much larger than in humans. ... Alanine transaminase (ALT): ALT level in blood is used for the diagnosis of liver disease and injury in human and veterinary medicine. ... Indeed, the m-values [The m-value refers to monomeric proteins] ... suggest a genetic effect of [single-nucleotide polymorphism (SNP)] BICF2P496164 in five breeds only: Belgian Shepherds, Cavalier King Charles Spaniel, Doberman, Finnish Lapphund, and Newfoundland. ... Belgian Shepherd and Cavalier King Charles Spaniel had lead SNPs that differed from the lead SNP in the meta-analysis (BICF2P496164) but they had very high linkage disequilibrium with BICF2P496164. They were considered as one signal. ... Stress during physical examination: We identified experiment wide significant association of stress during physical examination. The m-value suggests that the same QTL [quantitative trait locus] effect segregates in Cavalier King Charles Spaniel and Dachshund at BICF2P1232291. ... [I]n both breeds dogs with an A allele were considered to be more stressed during physical exam. There are no protein coding genes in this locus. ... We identified an experimental-wide association with stress during physical examination at chromosome 1. Two breeds, Cavalier King Charles Spaniels and Dachshunds, showed the same tendency. Dogs with the A allele of BICF2P1232291 showed more stress during physical examination. ... Morphometric measurements. In the meta-analyses on morphometric measurements, four genome-wide associations were identified for the morphometric measurements C (height at withers), D (maximal chest diameter), and E (body length). ... The pattern between Morphometric parameter E (body length) and BICF2P67088 at the IGF1 locus was less clear but the lead SNP was fixed to a C allele with a smaller value in the smallest breed, the Cavalier King Charles Spaniel. ... These findings illustrate the importance of performing meta-analysis after breed-specific GWAS to reveal the genetic contribution to individual differences in clinically important measurements, which would lead to improvement of veterinary medicine.
The effect of inbreeding, body size and morphology on health in dog breeds. Danika Bannasch, Thomas Famula, Jonas Donner, Heidi Anderson, Leena Honkanen, Kevin Batcher, Noa Safra, Sara Thomasy, Robert Rebhun. Canine Med. & Genetics. December 2021; doi: 10.1186/s40575-021-00111-4. Quote: Background: Dog breeds are known for their distinctive body shape, size, coat color, head type and behaviors, features that are relatively similar across members of a breed. Unfortunately, dog breeds are also characterized by distinct predispositions to disease. We explored the relationships between inbreeding, morphology and health using genotype based inbreeding estimates, body weight and insurance data for morbidity. ... A large dataset (227 breeds) of median heterozygosity values (H) was obtained through commercial DNA testing of 49,378 dogs. ... Results: The average inbreeding based on genotype across 227 breeds was Fadj =0.249 (95% CI 0.235–0.263). ... Cavalier King Charles Spaniel: Fadj: 0.411. ... Strikingly few breeds (N = 12) had low inbreeding values (< 0.10). The breeds with the lowest levels of inbreeding were mostly landrace breeds or breeds with recent cross breeding. To put the inbreeding values in context, the breeding of two first cousins produces F = 0.0625, two half siblings F = 0.125 and two full siblings or parent-offspring F = 0.25. ... The inbreeding values within dog breeds were very high, with the mean being 0.24, just below the coefficient of inbreeding obtained from breeding full siblings. The breeds with low inbreeding included recent cross breeds (Tamaskan Dog, Barbet and Australian Labradoodle) and landrace breeds (Danish-Swedish Farmdog, Mudi and Koolie), supporting the notion that high inbreeding is a result of closed stud books or small numbers of founders or both. It also demonstrates that it is possible to have consistent breed type without inbreeding. ... One must consider that the majority of dog breeds displayed high levels of inbreeding well above what would be considered safe for either humans or wild animal populations. ... There were significant differences in morbidity between breeds with low and high inbreeding (H=16.49). There was also a significant difference in morbidity between brachycephalic breeds and non-brachycephalic breeds and between functionally distinct groups of breeds (H=14.95). Morbidity was modeled using robust regression analysis and both body weight and inbreeding were significant (r2 = 0.77). Smaller less inbred breeds were healthier than larger more inbred breeds. Conclusions: In this study, body size and inbreeding along with deleterious morphologies contributed to increases in necessary health care in dogs.
Investigating the relationship between inbreeding and life expectancy in dogs: mongrels live longer than pure breeds. Fernando Mata, Andreia Mata. Peer J. July 2023; doi: 10.7717/peerj.15718. Quote: This study aimed to investigate the establishment of relationship between inbreeding and life expectancy in dogs. A dataset of N = 30,563 dogs sourced from the VetCompass™ Program, UK was made available by the Royal Veterinary College, University of London, containing information about breed and longevity and was subject to survival analysis. A Cox regression proportional hazards model was used to differentiate survivability in three groups of dogs (mongrel, cross-bred and pure breed). ... A total of N=30,563 entries were found in the original dataset, which after data cleansing and elimination of outliers, resulted in a sample of N=30,470 dogs (n=2,406 mongrel, n=3,962 crossbred, and n=24,102 pure breed) [including 1,004 cavalier King Charles spaniels]. ... The model was found highly significant and we found that mongrel dog had the highest life expectancy, followed by cross-bred dogs with only one purebred ancestor and purebred dogs had the lowest life expectancy. A second Cox regression was also found highly significant differentiating the lifespan of different dog breed and correlating positively the hazard ratio and the Genetic Illness Severity Index for Dogs (GISID). The results show that survivability is higher in mongrel dogs followed by cross-bred with one of the ancestor only as a pure breed, and pure breed dog have the highest morbidity level. Higher morbidity is associated with higher GISID scores, and therefore, higher inbreeding coefficients. These findings have important implications for dog breeders, owners, and animal welfare organizations seeking to promote healthier, longer-lived dogs.
Dog Breeding Practices must Change: Welfare cost of cuteness. Clare Rusbridge. Univ. Of Surrey. May 2024; doi: 10.13140/RG.2.2.12316.81284. Quote: Despite clear evidence that the breeding practices ofcertain dog breeds lead to animals suffering from arange of different conformational malformations causing pain, discomfort and life limiting conditions, some breed clubs have followed societal fashion for‘cute’ dogs, prioritising the aestetics, rather than the health of animals. Many breeds are facing painful and life-limiting conditions, requiring expensive veterinary care, which are caused by poor and outdated breeding practices. University of Surrey’s research on canine Chiari-like malformation (CM) and syringomyelia (SM) has shone a spotlight on the plight of the Cavalier King Charles Spaniel (CKCS) and other brachycephalic (flat-faced) dogs and the urgentneed for change. ... There are many health conditions caused by inbreeding. Shining a spotlight on the popular Cavalier King Charles Spaniel (CKCS), as a prime example of a dog which has been bred from a very small gene pool, is illustrative of why practice needs to change. It is common for CKCS to suffer from multiple health conditions, the median is six conditions per dog at 6 years old. CKCS are known to suffer from the painful disease Chiari-like malformation (CM) and syringomyelia (SM). CM and SM are inherited, and the complex inheritance involves several unknown genes. Syringomyelia is characterised by the development of fluid-filled cavities within the spinal cord. In dogs this is often associated with a complex developmental malformation of the skull and upper neck vertebrae called Chiari-like malformation. CM is a developmental condition which causes a change in the shape of the skull and the bones at the top of the neck, resulting in a reduced space for the brain and spinal cord to fit into. The conditions affect several small brachycephalic (short-nosed) dog breeds but is more seen in the CKCS and Chihuahuas. ... Unsurprisingly, pain can cause behavioural problems, freque centres suffer from Chiari-pain and syringomyelia. The sad fact is that the Cavalier breed is in deep trouble. No amount of selective breeding will help the health of these dogs, there are simply too few healthy specimens left. ... Unsurprisingly, pain can cause behavioural problems, frequently leading to Cavaliers being surrendered to rescue centres. 70% of dogs surrendered into Cavalier breed specific rescue the health of these dogs, there are simply too few healthy specimens left. ... Policy Recommendations: The UK Government must uphold the Animal Welfare Act, 2006. ... The system for breeding dogs is outdated and must change. ... Health testing dogs is not sufficient, breeding is a science, not an amateur endeavour. Cattle breeders already use estimating breeding values. This is the right tool to manage most inherited diseases, dog breeders must do the same. ... Breeding with small genetic populations with closed stud books is not sustainable. Crossbreeding and opening the breed registers is the only way to improve animal welfare and save certain breeds from extinction. If we want some breeds to survive, we have to accept they will need to look different to the modern-day appearance. ... Demand for puppies should be met by stable supply from within a country’s own market. ... Better regulation of dog breeding is the way forward, rather than banning breeds.
Identification of genes associated with longevity in dogs: 9 candidate genes described in Cavalier King Charles Spaniel. Evžen Korec, Lenka Ungrová, Josef Kalvas, Jirí Hejnar. Vet. & Anim. Sci. December 2024; doi: 10.1016/j.vas.2024.100420. Quote: In the past years, dogs have served as a convenient natural model organism for longevity due to their similarity with humans concerning not only their environment but also the diseases and complications occurring in older age. Since many dog breeds have significantly shorter lifespan than their closely related breeds, identification of genes associated with longevity may help to elucidate its background and serve as a possible tool for selective breeding of long-living dogs. This genome-wide association study (GWAS) was undertaken to identify the candidate genes associated with longevity in Cavalier King Charles Spaniel individuals that have reached the age of more than 13 years. ... Buccal swab samples from purebred, FCI registered, CKCS dogs were collected during the year 2023 with the help of registered breeders and kennels in the Czech Republic. For the purpose of this research, samples were divided into two groups defined by the age of the dogs examined. For the reference group, we sampled dogs at the age between 2 and 7 years, which present the first quartile in the range of mortality age in the CKCS. The group of long-lived dogs contained samples from individuals older than 13 years, which presents the upper quartile in the range of mortality age in CKCS. ... Out of the 48 genotyped dogs, 41 (24 long-lived and 17 reference) passed the filtering steps. 7 dogs were excluded due to the low genotyping rate. ... We described 15 SNPs localized in nine genes: B3GALNT1, NLRP1 like, PARP14, IQCJ-SCHIP1, COL9A1, COL19A1, SDHAF4, B3GAT2, and DIRC2 that are associated with longevity in purebred Cavalier King Charles Spaniels. These results are promising for future research and possible selective breeding of companion dogs with extended lifespan. ... The current knowledge shows that all the genes with SNPs described in this study as associated with longevity in CKCS could directly or indirectly influence health and prolong life. We identified genes associated with common longevity-influencing factors such as cancer, immunity, DNA damage, cellular repair, and oxidative stress. We also found genes that may play a role in the tissue structure and formation. Most importantly, longevity-associated SNPs were found in genes that play a role in heart diseases, which are the major cause of death in the CKCS. We described SNPs in two collagen genes associated with longevity in the CKCS. Collagens were previously described to undergo morphological changes in the dogs affected with mitral valve disease, and changes in their expression in affected CKCS to have a direct effect on longevity. Our results show that the detected longevity-associated SNPs could also serve as potential markers of diseases. In addition, the prolongation of healthspan– disease-free period of life, would directly influence lifespan of the dogs. The proper separation of longevity markers and disease markers will be possible by further investigating these genes and their function in larger datasets and in interbreed analysis. This will allow us to assess the importance and significance of longevity-associated genes within and among breeds.


CONNECT WITH US